 Sadly, India is known as the “Diabetes Capital of the World.” Right now, around 101 million people in India have diabetes. Experts think this number could grow to 135 million by 2045.
Sadly, India is known as the “Diabetes Capital of the World.” Right now, around 101 million people in India have diabetes. Experts think this number could grow to 135 million by 2045.
This means that about 17% of all people with diabetes in the world live in India, showing that diabetes is a big health problem for the country.
The main reasons are high calorie, high-fat, and high-sugar diets, physical inactivity, genetic factor, obesity and lack of awareness. For patients who struggle to manage their diabetes with diet, exercise, or medication and are at high risks for other serious health conditions, metabolic surgery is a great solution.
What is Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes?
Metabolic surgery, a type of bariatric surgery, is a powerful approach to treating type 2 diabetes, especially in people who are overweight.
This procedure goes beyond weight loss; it alters how the body handles sugar and insulin by changing the stomach and intestines. As a result, it can significantly reduce or even reverse type 2 diabetes, making it a proven solution.
How Metabolic Surgery Works
Metabolic surgery aids in weight loss and changes the hormones in the gut that control blood sugar levels.
This leads to better insulin sensitivity and more stable blood sugar control.
While researchers are still exploring exactly how this surgery improves type 2 diabetes, some key mechanisms include:
Weight Loss: Reduces fat that affects metabolism.
Increased Hormones: GLP-1 hormone levels increase, improving insulin sensitivity.
Faster Gastric Emptying: Nutrients reach the intestines quicker, aiding metabolism.
Changes in Bile Acids and Gut Bacteria: These changes enhance metabolic function.
How Effective is Metabolic Surgery?
Metabolic surgery has been shown to be highly effective in treating type 2 diabetes.
Here are some statistics from studies:
- 77% of Patients: Experience diabetes remission within 14.6 months after surgery.
- 72% at 2 Years: Achieve remission, compared to 21% who rely only on medication.
- 49% of RYGB Patients: Reach key health goals (HbA1c under 7%, LDL under 100 mg/dL, and blood pressure under 130/80 mmHg) within a year, compared to 19% with medical therapy alone.
- Even with a BMI under 35: Patients can see improvements in glucose and lipid levels after surgery.
Differences Between Metabolic Surgery and Bariatric Surgery
Though often used interchangeably, metabolic surgery and bariatric surgery have distinct purposes:
- Definition: Bariatric surgery is designed to help people with obesity lose weight, while metabolic surgery, a type of bariatric surgery, focuses specifically on treating metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes, regardless of a patient’s weight.
- Patient Criteria: Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for those with a BMI over 35 or a BMI over 30 with other health issues. Metabolic surgery can be suitable for individuals with a BMI as low as 30, especially if they have type 2 diabetes.
- Goals: The primary goal of bariatric surgery is weight loss. For metabolic surgery, the focus is on improving or curing metabolic conditions like diabetes, even if weight loss is not the main objective.
- How They Work: Bariatric surgery mainly reduces food intake or absorption, while metabolic surgery also changes gut hormones and how the body manages blood sugar.
Typical Candidates for Metabolic Surgery
Ideal candidates for metabolic surgery usually have type 2 diabetes and are overweight or obese. Here’s when it’s recommended:
- BMI of 30 or Higher: For Asian patients, a BMI of 27 or more might be sufficient due to different body types and health risks.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes: Patients who struggle to manage their diabetes with diet, exercise, or medication and face high risks.
- Other Health Issues: Those with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or sleep apnea, which complicate diabetes management, may benefit from metabolic surgery.
- Lifestyle Commitment: Patients must be willing to make lifelong changes in their diet and exercise to maintain weight loss and prevent diabetes from returning.
- Health Status: While there’s no strict age limit, candidates are usually adults in good health, aside from their metabolic issues. A thorough health check is done to ensure surgery is safe.
In short, people with a BMI of 30 or higher, who have poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and are ready to change their lifestyle, are good candidates for metabolic surgery.
This surgery is a recognized treatment option for diabetes, especially when other methods haven’t worked.
Types of Metabolic Surgery
Here are some common types of metabolic surgery:
- Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB): This procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach. It leads to reliable weight loss with fewer risks.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this surgery, about two-thirds of the stomach is removed, leaving a narrow, sleeve-shaped stomach. This change in gut hormones and metabolism promotes weight loss and can lead to diabetes remission.
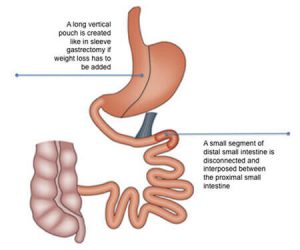
- Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S): A newer version of the duodenal switch surgery, it combines a sleeve gastrectomy with rerouting of the small intestine, reducing calorie absorption. It has excellent results for weight loss and diabetes remission with fewer side effects.
By choosing metabolic surgery at the Laparo-Obeso Centre with experts like Dr. Shashank Shah, patients can explore a life-changing option for managing and potentially reversing type 2 diabetes.
To know more about metabolic surgery to improve or reverse your type 2 diabetes, click here to schedule your consultation.

